The national minimum wage is a critical factor in shaping employment trends and labor markets. As we move into 2024, changes to the national minimum wage are expected to have significant implications for workers, employers, and the broader economy. Here’s an exploration of how the 2024 national minimum wage is likely to influence employment trends and the future of work.
Read more Emmanuel Macron: The Visionary Leader Reshaping France’s Future
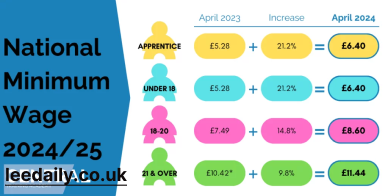
Overview of the 2024 National Minimum Wage
The national minimum wage for 2024 reflects adjustments made to ensure fair compensation for workers and to address the rising cost of living. Governments typically review and adjust the minimum wage annually, taking into account factors such as inflation, cost of living, and economic conditions.
Key Impacts on Employment Trends
1. Wage Growth and Employee Purchasing Power
- Increased Purchasing Power: A higher minimum wage improves workers’ purchasing power, allowing them to spend more on goods and services. This can lead to increased consumer demand and potentially stimulate economic growth.
- Reduction in Income Inequality: Raising the minimum wage helps reduce income inequality by ensuring that lower-wage workers receive fair compensation for their labor.
2. Effects on Small Businesses
- Increased Operational Costs: Small businesses, particularly those with tight profit margins, may face increased operational costs due to higher wage expenses. This could lead to adjustments in business strategies, such as reducing staff hours or increasing prices.
- Adapting Business Models: Some small businesses may adopt technology or automation to offset higher labor costs, potentially leading to changes in the nature of work and job roles.
3. Employment Levels and Job Market Dynamics
- Potential Job Losses: In some cases, employers may reduce hiring or lay off workers to manage increased labor costs. This could impact employment levels, particularly in low-wage industries.
- Increased Job Attraction: Conversely, higher wages may attract more job seekers to low-wage sectors, increasing competition for available positions and potentially improving job quality.
4. Impact on Workforce Participation
- Encouraging Workforce Participation: A higher minimum wage may encourage more individuals to enter the workforce, including those who may have previously been discouraged by lower wages.
- Reducing Informal Work: By providing a more attractive wage, the formal job market may draw workers away from informal or under-the-table employment.
5. Influence on Employee Retention and Motivation
- Improved Retention: Higher wages can enhance employee satisfaction and reduce turnover rates, as workers are more likely to stay with employers who offer competitive compensation.
- Increased Motivation: Better pay can lead to increased motivation and productivity among employees, contributing to overall business performance.
Broader Economic and Social Implications
1. Economic Growth
- Stimulating Demand: Higher wages contribute to greater consumer spending, which can boost demand for goods and services and support economic growth.
- Inflationary Pressures: While increased wages can stimulate demand, they may also lead to higher prices for goods and services, contributing to inflationary pressures.
2. Social Equity
- Addressing Poverty: Raising the minimum wage is a tool for addressing poverty and improving the quality of life for low-wage workers and their families.
- Promoting Fair Labor Practices: It reinforces the principle of fair compensation for work, supporting a more equitable labor market.
Future Considerations
As we look ahead, the ongoing evolution of the minimum wage will continue to influence employment trends and the future of work. Key considerations include:
- Policy Adjustments: Governments may need to balance minimum wage increases with other economic policies to manage potential impacts on businesses and employment.
- Technological Advancements: The integration of technology and automation may play a role in how businesses adapt to higher wage costs and manage workforce changes.
Conclusion
The 2024 national minimum wage represents a pivotal shift in the landscape of employment and labor markets. By improving wages, addressing income inequality, and influencing business practices, it has the potential to shape the future of work in significant ways. While there are challenges to navigate, the positive impacts on worker welfare, economic growth, and social equity highlight the importance of thoughtful and responsive wage policies.